Prevent as much as 80% of SPAM from ever getting to your Exchange mail server.
Quick:
Exchange System Manager (ESM), Global Settings, Message Delivery (properties):
-Sender Filtering Tab, Check Box “Filter messages with blank sender”
-Recipient Filtering Tab, Check box “Filter recipients who ar not in the Directory”
-Sender Filtering Tab, Check Box “Filter messages with blank sender”
-Recipient Filtering Tab, Check box “Filter recipients who ar not in the Directory”
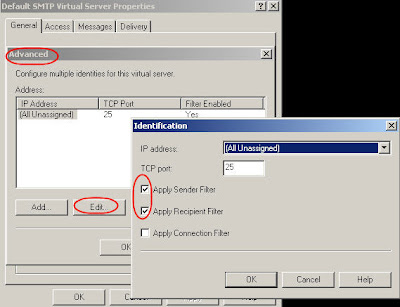
ESM, Administrative Groups, Servers, YourSvrName, Protocols, SMTP, Default SMTP Virtual Sever (properties), General tab, Advanced… button, Edit connection, Check Boxes “Apply Sender Filter” and “Apply Recipient Filter”
Visual:

Visual:


Reduction in load as seen by Spam Software
Learning:
-------- Text From Link -------
Author: Amit Zinman
The Hidden Power of Sender and Recipient Filtering
Filtering in Exchange 2003 can be a powerful tool in the right hands. It can help you to protect your mail server, especially in a single server or branch scenario when no mail relay is provided and ease the load off your regular anti virus and anti spam packages if it is used right. The mail filtering capabilities in Exchange 2003 are often overlooked, especially for companies who bought more snazzy anti-spam packages and think nothing much of the seemingly rudimentary options provided by Exchange 2003. However, using these options can help ease the load off your server and possibly your anti-virus and anti-spam packages if used wisely because the Sender and Recipient Filtering options can drop connections for Exchange 2003. This means that connections made by the server trying to deliver the mail item is blocked by the SMTP engine. This is faster and more efficient than evaluating the mail after it is received and already in the mail queue.
Sender Filtering
Creation of the sender filter is done by using the Sender Filtering tab in the Message Delivery Properties dialog box in Global Settings.
These are the recommended settings and will ensure that connections are dropped for mails with blank senders and the manually specified senders.
You can specify asterisk ("*") wildcard in the senders e-mail address to block e-mail from a whole domain. For example, *@spamspam.com will block all e-mail from spamspam.com.
Let''s consider another scenario. You suspect someone is sending e-mails to a spy within your company and you want to intercept these mails before they hit the spy''s mailbox, and still be able to read them. To be able to do this, configure Sender Filtering as follows:
You can specify asterisk ("*") wildcard in the senders e-mail address to block e-mail from a whole domain. For example, *@spamspam.com will block all e-mail from spamspam.com.
Let''s consider another scenario. You suspect someone is sending e-mails to a spy within your company and you want to intercept these mails before they hit the spy''s mailbox, and still be able to read them. To be able to do this, configure Sender Filtering as follows:
This will cause messages from the specified send to go to the filter directory under the mail root SMTP virtual server directory.
You can open the file using notepad to view the mail item contents. If you change extension to "EML" it will also open in Outlook Express, allowing you to view HTML content.This option also exists in Exchange 2000 where it is simply called "Filtering".
Recipient Filtering
Creation of the recipient filter is done by using the Recipient Filtering tab in the Message Delivery Properties dialog box.
As you know archiving options are available for recipient filtering.
The "Filter recipients who are not in the Directory" option, not enabled by default is the single most overlooked important setting. It allows you to fight dictionary and other SPAM attacks. Spammers send mail to users they hope exist in your domain, sometimes hoping to learn if they exist by reading NDRs generated by Exchange, and sometimes just sending to common names, or running through a dictionary of names.
Let''s evaluate such a scenario. A virus hits one of your customers' computers. The virus opens a contact for a user in your domain. It starts viruses to users in your domain by using names and the first letter of the alphabet. So, you're now getting a lot of e-mails containing a virus sent to "johna", "johnb", "johnc", etc.If you filter out recipients that are not in the directory then your antivirus engine does not have to handle all these messages. Instead, it only has to handle messages actually addressed to people in your organization, thus, lowering the CPU and disk space use required by your Antivirus package.
The "Filter recipients who are not in the Directory" option, not enabled by default is the single most overlooked important setting. It allows you to fight dictionary and other SPAM attacks. Spammers send mail to users they hope exist in your domain, sometimes hoping to learn if they exist by reading NDRs generated by Exchange, and sometimes just sending to common names, or running through a dictionary of names.
Let''s evaluate such a scenario. A virus hits one of your customers' computers. The virus opens a contact for a user in your domain. It starts viruses to users in your domain by using names and the first letter of the alphabet. So, you're now getting a lot of e-mails containing a virus sent to "johna", "johnb", "johnc", etc.If you filter out recipients that are not in the directory then your antivirus engine does not have to handle all these messages. Instead, it only has to handle messages actually addressed to people in your organization, thus, lowering the CPU and disk space use required by your Antivirus package.
Enabling Filtering
When you change the filtering settings in Exchange 2003 you might notice the following message:
------Message regarding need to manually enable filtering ----------
This message appears because filtering is disabled by default the SMTP virtual server. To enable it, using Exchange System Manger expand Servers, expand the server that you want, expand Protocols, and then expand SMTP. Right-click the SMTP virtual server on which you want to apply the filter, and then click Properties. In the SMTP Virtual Server Properties, on the General tab, click Advanced.
Conclusion
Filtering in Exchange 2003 can be a powerful tool in the right hands. It can help you to protect your mail server, especially in a single server or branch scenario when no mail relay is provided and ease the load off your regular anti virus and anti spam packages if it is used right.
---------End Text From Link -------

No comments:
Post a Comment